Chapter 10 Data
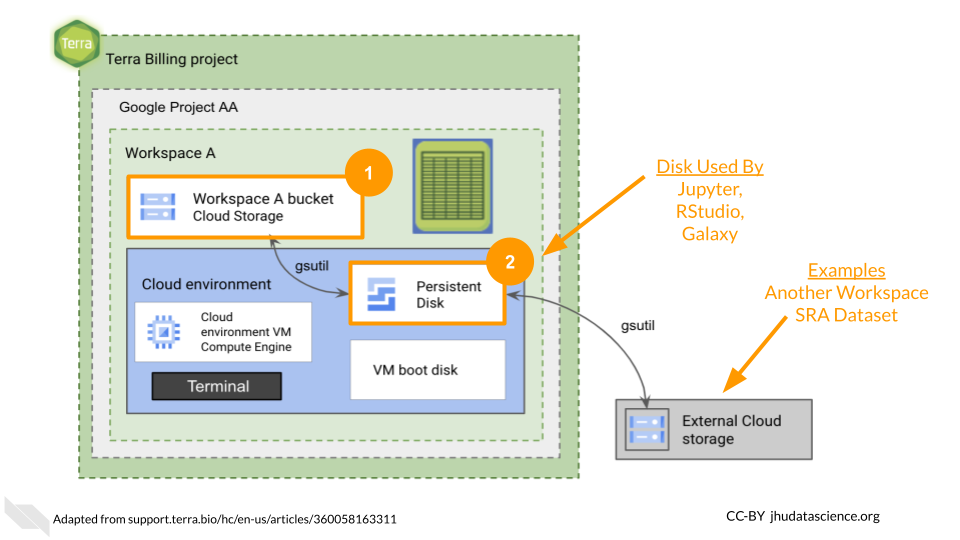
Data is stored by Workspaces in two different locations: the Workspace Bucket and the Persistent Disk.
The Workspace Bucket is a special Google Cloud Storage bucket that is governed by the built-in AnVIL security policies. This durable and scalable storage location is suitable for both raw data as well as analysis outputs that need to be preserved and/or shared.
In contrast, Persistent Disks provide a working directory for Cloud Environments that run Jupyter, RStudio, and Galaxy. Input data can be localized to Persistent Disks for analysis while output data can be transferred to the Workspace Bucket for more reliable long term storage.
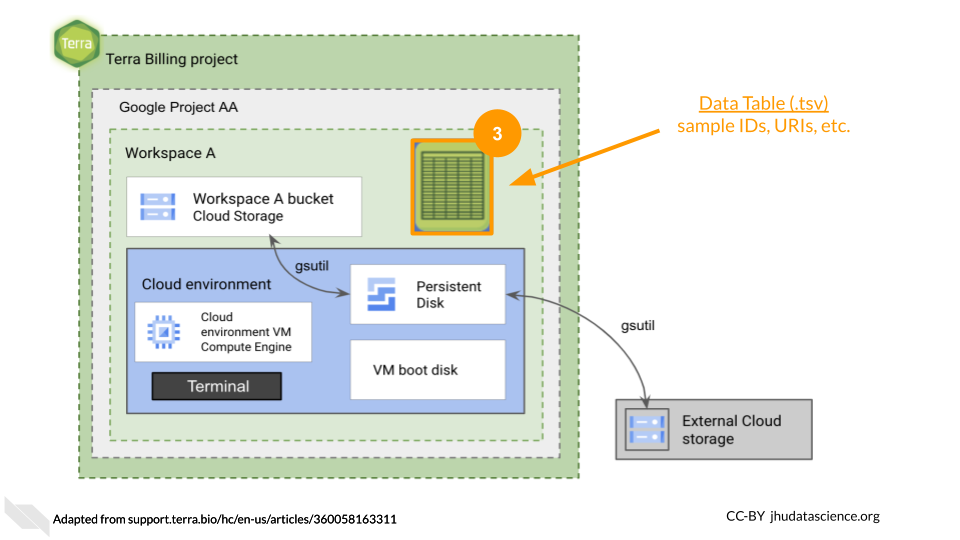
Data Tables provide a way to organize data and metadata, including URI links to storage buckets. These tables are a convenient way to organize input for analyses as well as tracking workflow outputs. More details can be found in the Terra documentation.
10.1 Bring Your Own Data
10.1.1 Overview
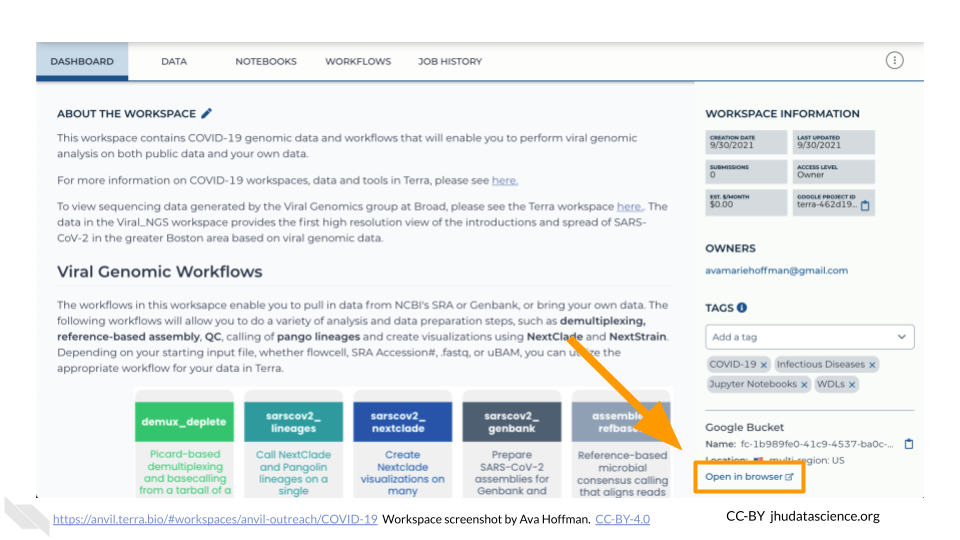
The starting point for bringing your own data to AnVIL is the Workspace Dashboard. At the bottom right, you’ll find the full path to the Google Bucket information corresponding to your Workspace. You can click the clipboard icon on the right to copy the name of your Workspace Bucket. You will be able to see any uploaded files by clicking the “Open in browser” link.
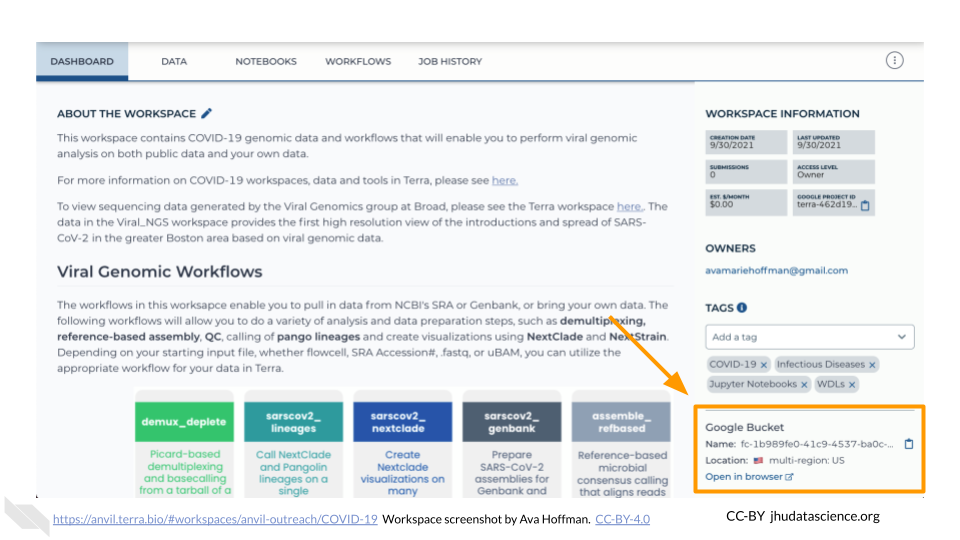
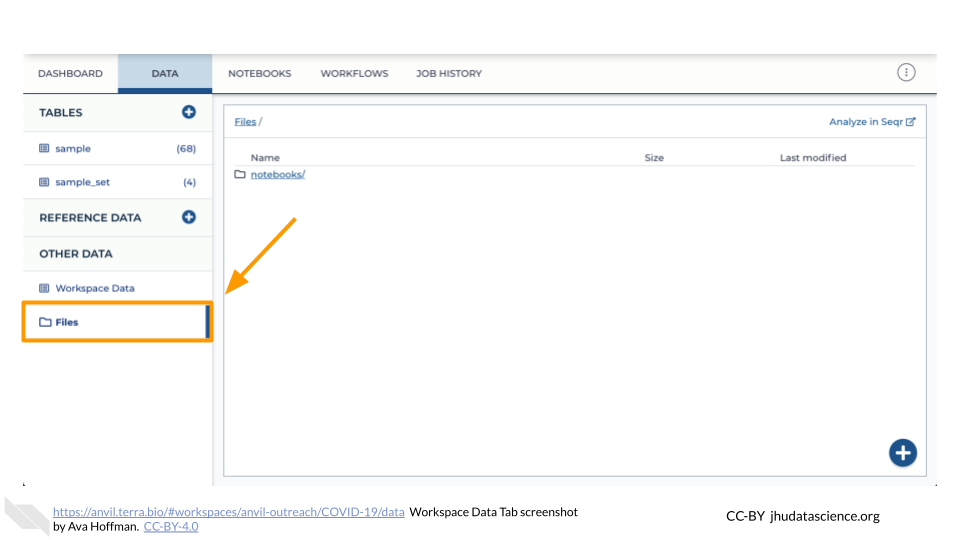
You can also see any uploaded files by clicking the “Files” directory at the bottom left in the Data Tab.
10.1.2 Browser: Upload Single Files
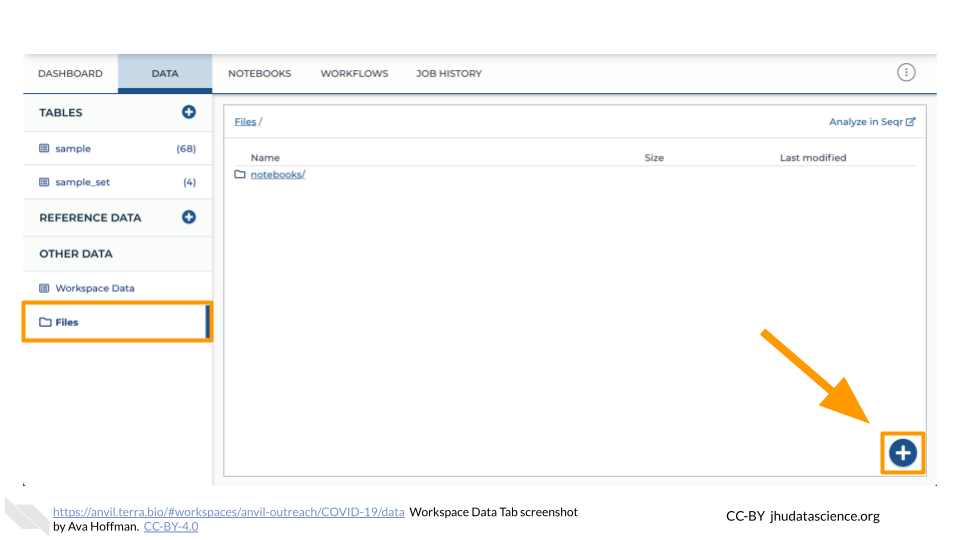
Click the “Files” directory at the bottom left of the Data Tab. Then click the “+” button in the bottom right corner of the screen. This will prompt a file browser on your local machine.
10.1.3 Browser: Upload Folders
Click the “Open in browser” link on the bottom right of the Workspace Dashboard Tab. This will open a new browser window or tab directed to your Workspace’s Google Bucket on the Google Cloud Platform.
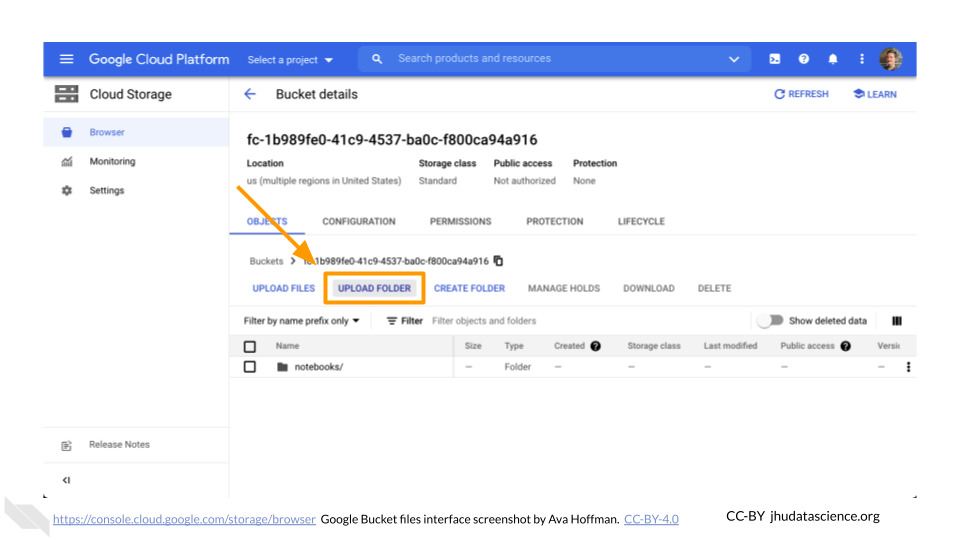
Here, you can upload files and manage your data and folders. You can also upload an entire folder by clicking on “UPLOAD FOLDER”.
10.1.4 gsutil: Local to Cloud
gsutil is a Python application that lets you access Cloud Storage from the command line in a terminal. The terminal you use can be run on your local machine (local instance) or built into the Workspace Cloud Environment.
10.1.4.1 Install gsutil on Your Local Computer or Local Server
Cloud SDK is a set of tools that you can use to manage resources and applications hosted on Google Cloud. These tools include the gsutil command-line tool.
- Ensure you have a terminal available.
- MacOS and Linux users have a terminal application available by default. Terminal applications are also available through third party software, such as RStudio.
- Windows users should download a terminal application, such as Putty.
- Install Cloud SDK following the appropriate link below:
- Test that Cloud SDK has been successfully installed by typing
gsutilin the terminal application prompt:
gsutilIf the installation was successful, you should see information about using gsutil that looks like the following:
Usage: gsutil [-D] [-DD] [-h header]... [-i service_account] [-m] [-o] [-q] [-u user_project] [command [opts...] args...]If the installation was not successful, you should see a warning that gsutil was not found. Please return to the installation steps to ensure they have been completed correctly.
command not found: gsutil10.1.4.2 Copy Files From Your Local Computer to a Workspace Bucket
The gsutil cp command allows you to copy data from one machine to another. On your local machine’s terminal, you should use the command in the following format:
gsutil cp where_to_copy_data_from/filename where_to_copy_data_toExample: To copy the file test.bam located on your local computer at users/name/data/ into the Workspace Bucket gs://ab5-27x on the cloud:
gsutil cp users/name/data/test.bam gs://ab5-27xRemember that you can easily copy the Workspace Bucket ID using the clipboard button on the Workspace Dashboard. Please see the gsutil cp documentation for more details, such as how to do parallel multi-threaded/multi-processing copying or copying an entire directory tree. The gsutil cp command can also be used to copy files from one Workspace Bucket to another (cloud-to-cloud copying).
10.2 Analyze Existing Data
In addition to bringing your own data, you can use existing data on AnVIL. Using the following resources can help you discover data to use in your analyses.
10.2.1 AnVIL Data Library
The Datasets Library is a good place to get started and familiarize yourself with existing data. Here, you can find curated datasets from thousands of participants. Some of these are open access (such as the 1000 Genomes dataset) while others will require you to request access.
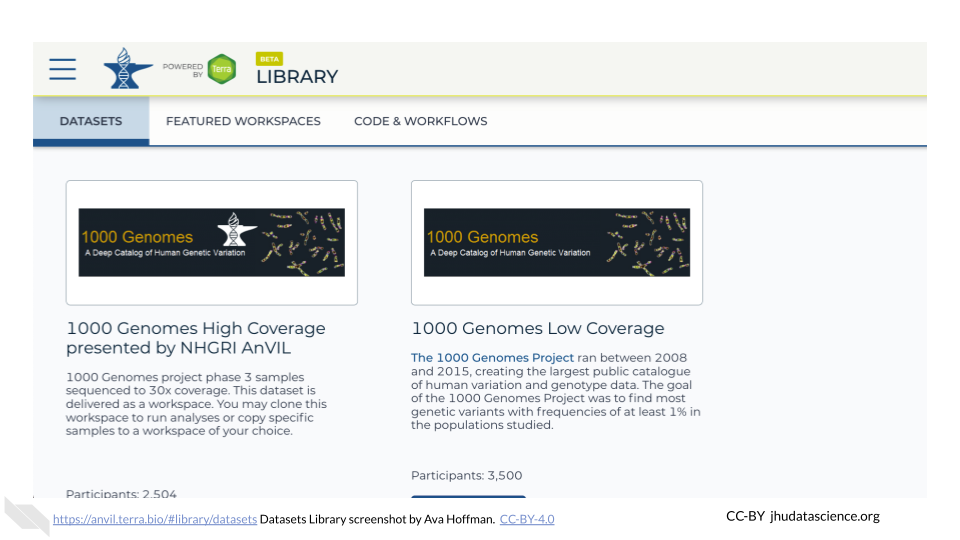
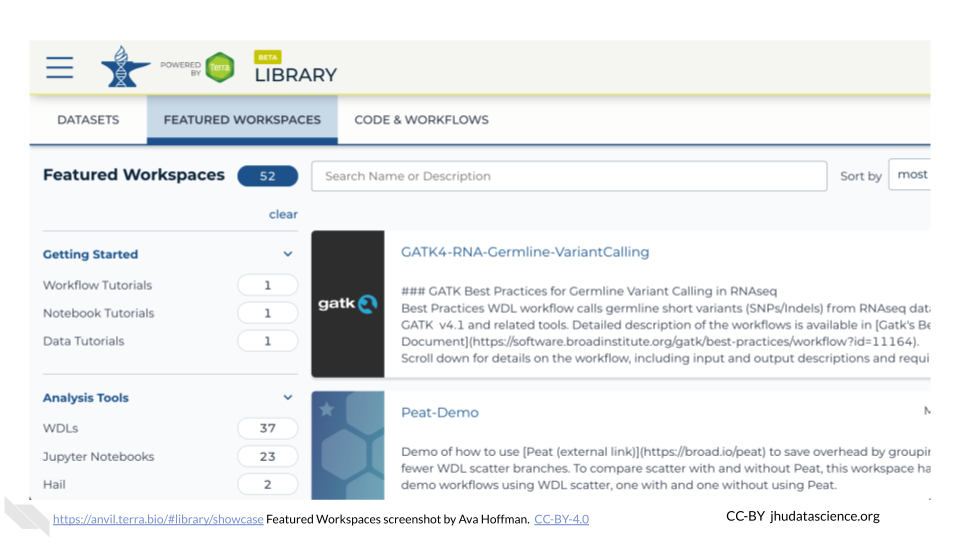
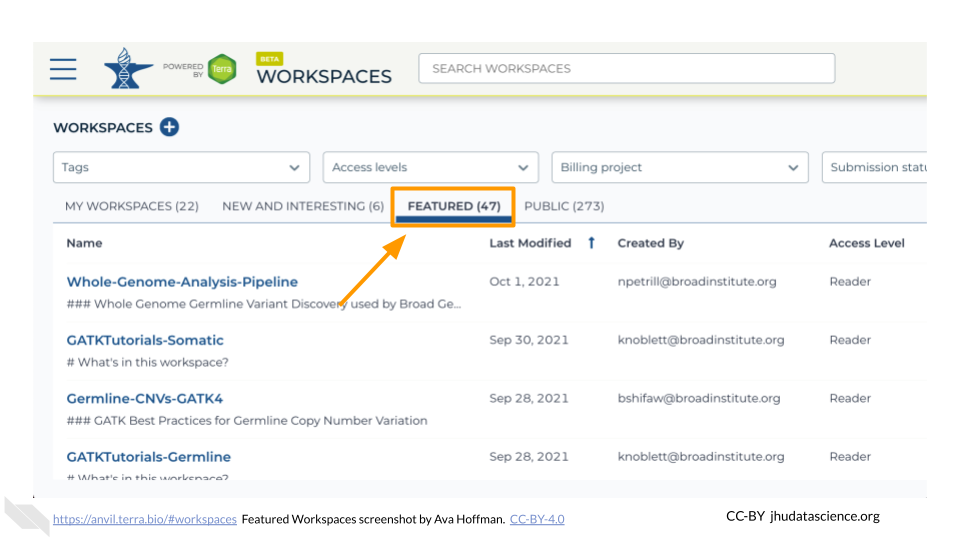
Taking a look at Featured Workspaces can get you started quickly. Remember that when you clone a Workspace, AnVIL automatically cross-links to the original data contained within the Data Tables.
10.2.2 AnVIL Dataset Catalog
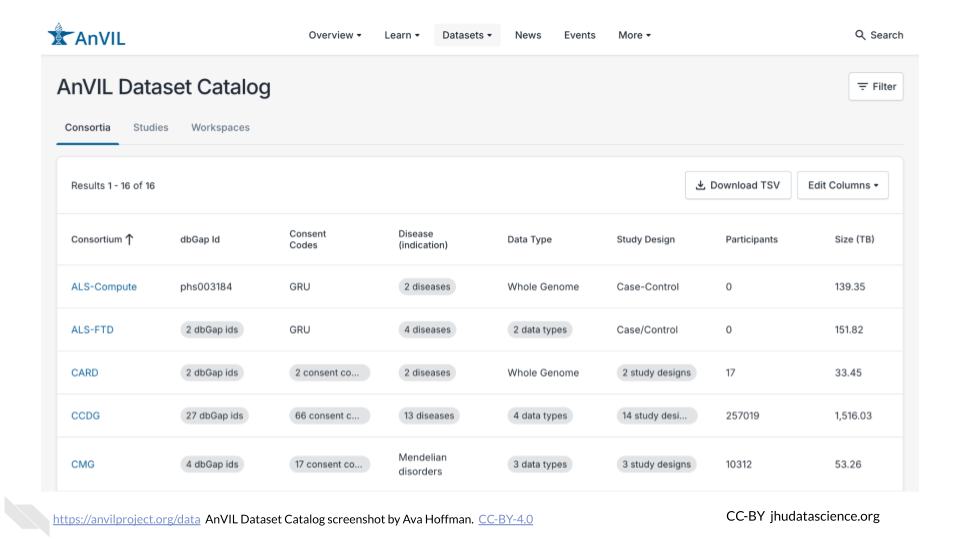
The AnVIL Dataset Catalog displays key NHGRI datasets accessible in AnVIL, such as the CCDG (Centers for Common Disease Genomics), CMG (Centers for Mendelian Genomics), eMERGE (Electronic Medical Records and Genomics), as well as other relevant datasets. You will need to coordinate access to controlled data.
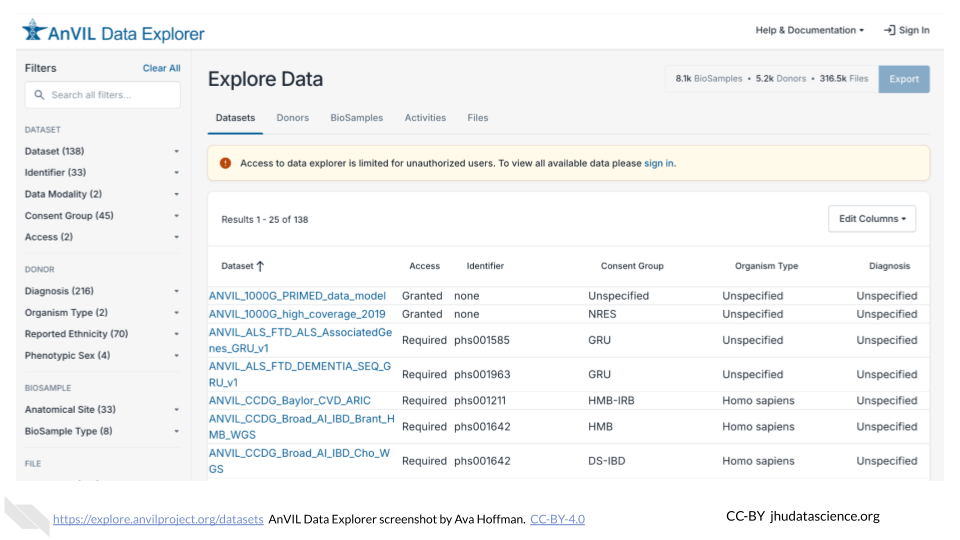
10.2.3 AnVIL Data Explorer
The AnVIL Data Explorer enables faceted searches of open and managed access datasets hosted in AnVIL, making it easier for researchers to find and custom-build cohorts.