- Introductions
- Class overview
- Getting R up and running
[Photo by Belinda Fewings on Unsplash]
[Photo by Belinda Fewings on Unsplash]
Carrie Wright
Assistant Scientist, Department of Biostatistics, JHSPH
PhD in Biomedical Sciences
Email: cwrigh60@jhu.edu
Website: https://carriewright11.github.io
Ava Hoffman
Research Associate, Department of Biostatistics, JHSPH
PhD in Ecology
Email: ava.hoffman@jhu.edu
Website: https://avahoffman.com
Candace Savonen
Research Associate, Department of Biostatistics, JHSPH
Masters in Neuroscience
Former Data Analyst for Childhood Cancer Data Lab
Email: csavone1@jhu.edu
Website: https://www.cansavvy.com/

Grant Schumock
PhD Candidate, Department of Biostatistics, JHSPH
BS in Nuclear Engineering
Email: gschumo1@jhmi.edu
Qier Meng
ScM Student, Department of Biostatistics, JHSPH
Bachelor’s Degree in Mathematics
Bachelor’s Degree in Neuroscience
Email: qmeng11@jhmi.edu
R is a language and environment for statistical computing and graphics
R is the open source implementation of the S language, which was developed by Bell laboratories in the 70s.
The aim of the S language, as expressed by John Chambers, is “to turn ideas into software, quickly and faithfully”

[source: http://www.r-project.org/, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/S_(programming_language), https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bell_Labs)]
In 1991 Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman at the University of Auckland, New Zealand began developing R
R is named partly after the first names of the first two authors and a play on the name of S.
R is both open source and open development

[source: http://www.r-project.org/, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/R_(programming_language)]
High level language designed for statistical computing
Powerful and flexible - especially for data wrangling and visualization
Free (open source)
Extensive add-on software (packages)
Strong community
 [source: https://rladies-baltimore.github.io/]
[source: https://rladies-baltimore.github.io/]
Little centralized support, relies on online community and package developers
Annoying to update
Slower, and more memory intensive, than the more traditional programming languages (C, Java, Perl, Python)
[source -School vector created by nizovatina - www.freepik.com]
What do you hope to get out of the class?
Why do you want to use R?
[Photo by Nick Fewings on Unsplash]
http://jhudatascience.org/intro_to_R_class
Materials will be uploaded the night before class
https://courseplus.jhu.edu/core/index.cfm/go/syl:syl.public.view/coid/16733/
End of class Survey - link in email.
[source - Banner vector created by pch.vector - www.freepik.com]
Homeworks and Final Project due by Wednesday, Jan 26, 2022 at 11:59pm EST.
If you turn homework in earlier this can allow us to potentially give you feedback earlier.
Note: Only people taking the course for credit must turn in the assignments. However, we will evaluate all submitted assignments in case others would like feedback on their work.
Install the latest version from: http://cran.r-project.org/
RStudio is an integrated development environment (IDE) that makes it easier to work with R.
More on that soon!
This course will involve moving files around on your computer and downloading files.
If you are new to this - check out these videos
If you have a PC: https://youtu.be/we6vwB7DsNU
If you have a Mac: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ao9e0cDzMrE
R jargon: https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/bbm%3A978-1-4419-1318-0%2F1.pdf
Package - a package in R is a bundle or “package” of code (and or possibly data) that can be loaded together for easy repeated use or for sharing with others.
Packages are sort of analogous to a software application like Microsoft Word on your computer. Your operating system allows you to use it, just like having R installed (and other required packages) allows you to use packages.
Function - a function is a particular piece of code that allows you to do something in R. You can write your own, use functions that come directly from installing R, or use functions from additional packages.
A function might help you add numbers together, create a plot, or organize your data. More on that soon!
sum(1, 20234)
[1] 20235
Argument - what you pass to a function
sum(1, 20234)
[1] 20235
round(0.627, digits = 2)
[1] 0.63
round(0.627, digits = 1)
[1] 0.6
Object - an object is something that can be worked with in R - can be lots of different things!
… many more
examples: temperature, length, count, color, category
examples: people, houses, viruses etc.
head(iris)
Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species 1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa 2 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa 3 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa 4 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa 5 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa 6 5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4 setosa
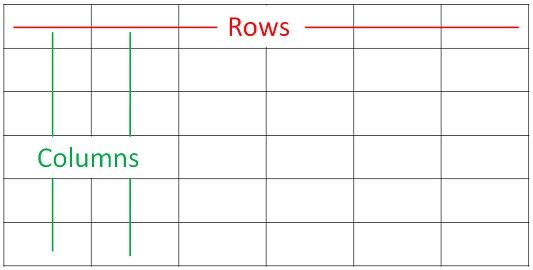 [source]
[source]
Sample = Row
Variable = Column
Data objects that looks like this is often called a data frame.
Fancier versions from the tidyverse are called tibbles (more on that soon!).
We will mostly show you how to use tidyverse packages and functions.
This is a newer set of packages designed for data science that can make your code more intuitive as compared to the original older Base R.
Tidyverse advantages:
- consistent structure - making it easier to learn how to use different packages
- particularly good for wrangling (manipulating, cleaning, joining) data
- more flexible for visualizing data
Packages for the tidyverse are managed by a team of respected data scientists at RStudio.

See this article for more info.
We have an R package called jhur that will make sure all the packages are installed.
You can just copy and paste the below code into your console - we’ll explain what it all means in the next day or two
install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("muschellij2/jhur")
Note it may take ~5-10 minutes to run.
Want more?
Tidyverse Skills for Data Science Book: https://jhudatascience.org/tidyversecourse/ (more about the tidyverse, some modeling, and machine learning)
Tidyverse Skills for Data Science Course: https://www.coursera.org/specializations/tidyverse-data-science-r
(same content with quizzes, can get certificate with $)
R for Data Science: http://r4ds.had.co.nz/
(great general information)
Open Case Studies: https://www.opencasestudies.org/
(resource for specific public health cases with statistical implementation and interpretation)
Dataquest: https://www.dataquest.io/
(general interactive resource)
Need help?
Various “Cheat Sheets”: https://www.rstudio.com/resources/cheatsheets/
R reference card: http://cran.r-project.org/doc/contrib/Short-refcard.pdf
R jargon: https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/bbm%3A978-1-4419-1318-0%2F1.pdf
R vs Stata: https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/bbm%3A978-1-4419-1318-0%2F1.pdf
R terminology: https://cran.r-project.org/doc/manuals/r-release/R-lang.pdf
Interested in Reproducibility?
Check out Candace’s courses: